Ethylene Oxide Processing
Ethylene oxide (also known as EO or EtO) is a low-temperature gaseous process broadly used to sterilize a wide variety of healthcare products, such as single-use medical devices. With the use of a vacuum-based process, EO sterilization can efficiently penetrate the surfaces of most medical devices, and its lower temperature makes it an ideal process for a variety of materials.
Ethylene Oxide (ETO) gas is one of the most common ways to sterilize medical devices. This safe, tightly controlled, highly regulated process is critical for preventing infections & ensuring patients have safe surgeries and medical treatments.
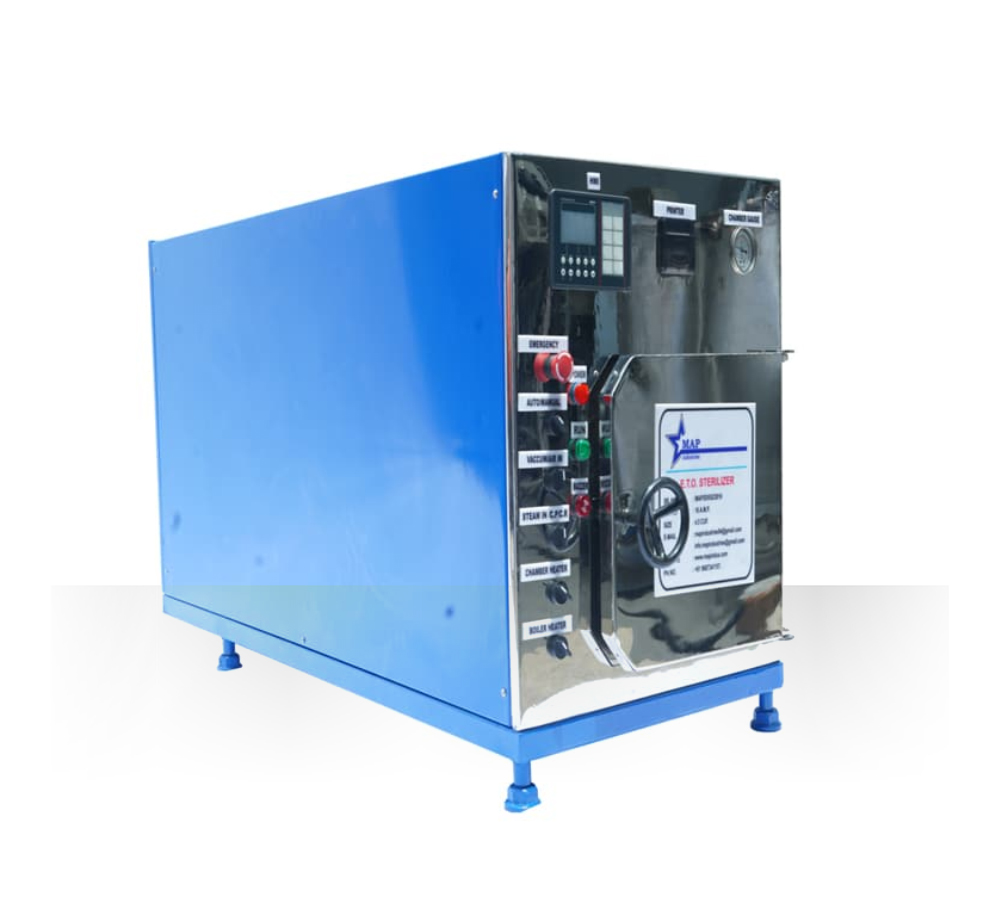

Ethylene Oxide Sterilization for Medical Devices Common Features:
An Ethylene Oxide (EO) sterilization validation is designed to assist the manufacturer in developing a sterilization process that delivers the appropriate sterility assurance level and ensures repeatability for each sterilizer medical product type developed by Map Industries in Ahmedabad, India.
The basic ETO sterilization for medical device cycles consists of five stages (i.e., humidification and preconditioning, gas introduction, evacuation, exposure, and air washes) and takes approximately 2 1/2 hours excluding aeration time.
Ethylene Oxide: Why Is Ethylene Oxide Used to Sterilize Medical Devices?
Ethylene oxide sterilization is an important sterilization method that manufacturers widely use to keep medical devices safe. For many medical devices, sterilizing ethylene oxide may be the only method that effectively sterilizes and does not damage the medical device during the ethylene sterilization process. Medical devices made from certain polymers (resin or plastic), glass, or metal, or that have multiple layers of packaging or hard-to-reach places (for example, catheters) are likely to be sterilized with ETO or ethylene oxide.